If you've got more than one VPS running then Linux server management can give you nightmares. SSHing into different servers to perform tasks like upgrading your packages or restarting services can be extremely tedious. However, managing multiple Linux servers doesn’t have to be complicated at all. There are many free open source linux server management tools you can install and use right away.
In this article, I will showcase the best Linux management software to make your life easier.
Note: This article has been reviewed by our team of experienced Linux administrators and DevOps engineers.
These Linux server management tools provide a wide range of management solutions, such as networking, monitoring, automation, and configuration management. These tools will streamline your operations, enhance efficiency, and ensure your servers are running smoothly.
Linux Management Software Tools
Here is the full list of the best Linux server administration tools:
- Cockpit
- Webmin
- Nagios
- Ansible
- Zabbix
- Puppet
- Chef
- SaltStack
- Kubernetes
- Grafana
- Prometheus
- phpMyAdmin
1) Cockpit
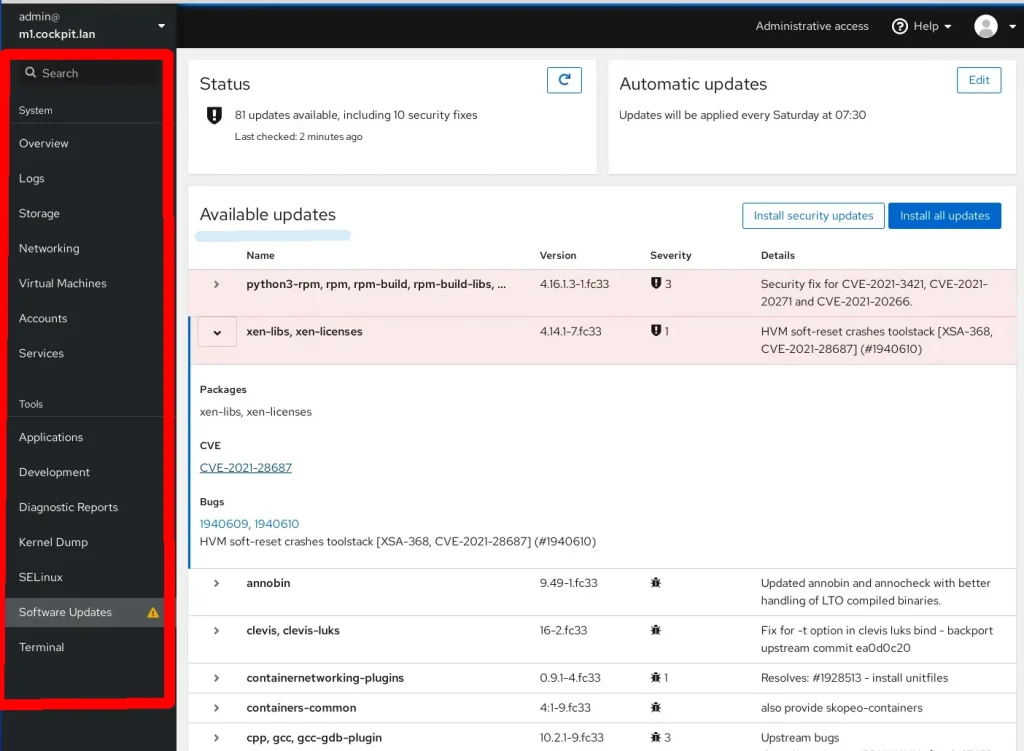
Developed by RedHat, the Cockpit for Linux project is an incredible Linux management software solution. It lets you manage services, add/remove users, set up networks, and much more via a web UI, or for the seasoned sysadmin, via the terminal.
Cockpit is self-contained, reuses existing privileges, and works with minimal addons.
You can start, stop, and restart services (irrespective of whether they were started through Cockpit or not).
Cockpit even supports container management giving you a list of available containers and their status (CPU/memory usage).
To manage multiple Linux servers, you can install the software on multiple machines and mark one as the master. From within the Machines option of your Cockpit dashboard, you can view details of the other VMs through neat graphs.
Cockpit is a Linux management software best used for:
- System Monitoring: Keeping an eye on system resources and performance in real-time.
- Service Management: Starting, stopping, and monitoring services and applications.
- Storage Management: Managing disks, RAID arrays, and network file systems.
- Network Configuration: Setting up and managing network interfaces, bridges, and bonds.
2) Webmin
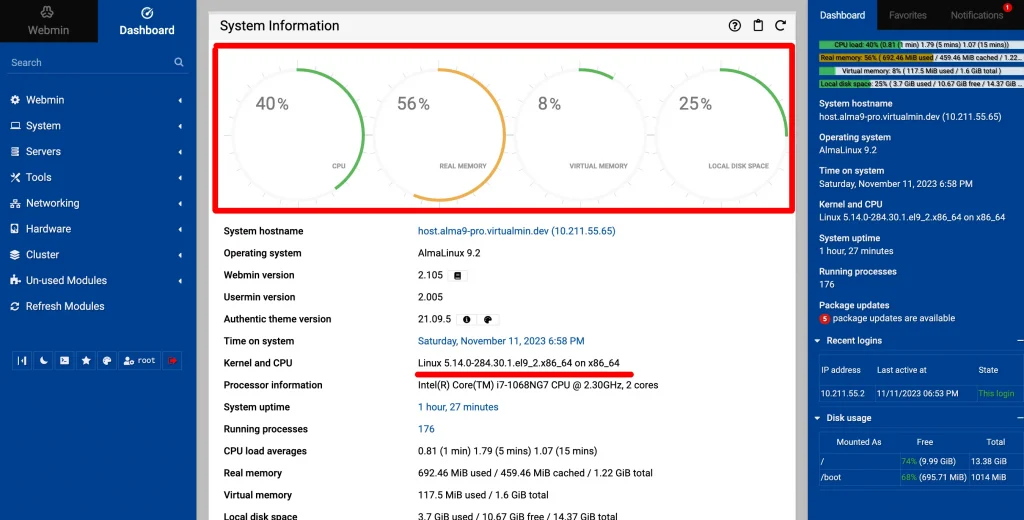
Webmin is another open-source tool for Linux server management. It allows you to manage multiple servers using a web interface instead of relying on the terminal.
Webmin provide an incredible range of features:
- Apache Web Server Support: Manages virtual hosts for domains, installs Apache modules, and minimizes HTTP headers for improved security.
- PHP Configuration: Allows configuration of PHP versions and variables from the dashboard.
- Graphical File Management: Enables easy editing, uploading, and downloading of files, as well as changing file permissions.
- MySQL and PostgreSQL Management: Allows management of databases after installing respective modules from the Webmin dashboard.
To manage multiple Linux servers, use the Cluster Webmin Servers module and install webmin on all your servers.
Identify one server as the main and connect to the others using username and a password. As a cluster, you can synchronize software updates, clone users and manage cron jobs.
In addition to allowing you to manage multiple servers for free, you can add on an additional product called VirtualMin (from the same company as WebMin) that helps with setting up virtual hosts, manage DNS zones.
Note: Setting up Webmin on your server can be overwhelming, that's why we offer a ready to use Webmin One-Click Application for our customers. Just visit our website, choose the server’s specifications that fit your needs, then select Webmin from the Choose OS dropdown menu. Webmin will then be installed in no time!
Webmin Tutorials
3) Nagios
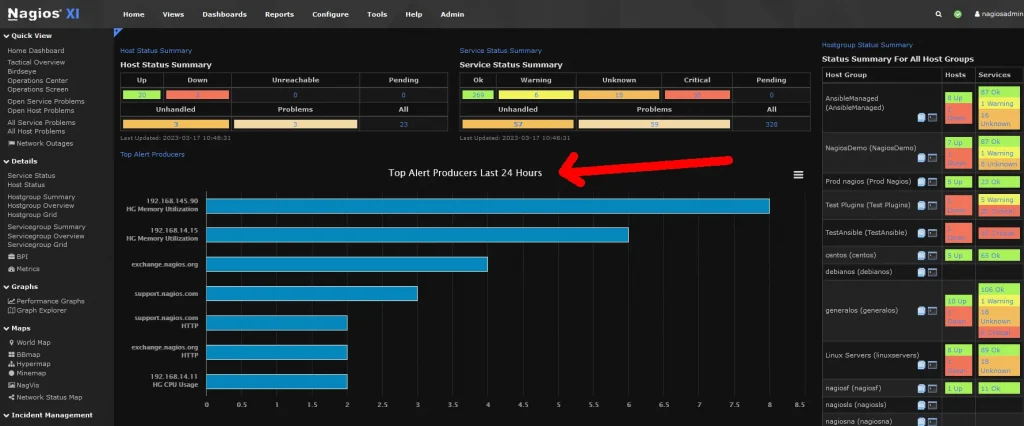
Nagios is one of the most popular open-source tools for monitoring networked systems. It can monitor server performance, network traffic, and even alert you to potential issues before they become critical. Nagios has an extensive plugin library that ensures it can be customized to fit your specific needs.
Nagios is a Linux management software best used for:
- Monitoring Server Performance: Keep an eye on CPU, memory, and disk usage.
- Tracking Network Traffic: Monitor bandwidth and detect potential issues.
- Alerting on System Issues: Receive notifications for outages and critical events.
- Ensuring Service Uptime: Monitor essential services to ensure they are running.
- Customizing Checks with Plugins: Extend functionality with a vast library of plugins.
- Visualizing Network Health: Use dashboards to get an overview of your network's status.
Nagios Cons
- Complex Initial Setup: Requires significant configuration to get started.
- Steep Learning Curve: Takes time to master due to its extensive features.
- Limited Scalability Without Plugins: May need additional plugins for large environments.
- Resource-Intensive on Large Networks: Can consume considerable resources as the network grows.
If you run gaming VPS servers, Nagios is super useful for monitoring the health and uptime of your servers. It can alert admins if there are connectivity or performance issues, ensuring minimal downtime for gamers.
4) Ansible
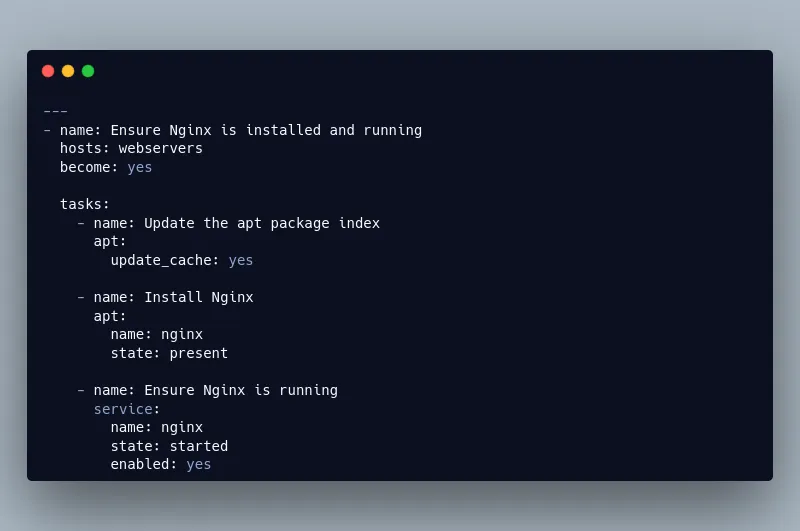
Ansible is a powerful automation tool that allows you to manage multiple servers from a single control point. Its simple, human-readable YAML syntax makes it easy to define your automation scripts, known as playbooks. Ansible is agentless, meaning you don’t need to install any software on your servers to manage them.
Ansible Benefits
- Agentless Architecture: No need to install additional software on your managed nodes, reducing overhead and simplifying management.
- Ease of Use: Simple YAML syntax allows you to write automation scripts quickly and read them easily.
- Scalability: Capable of managing large numbers of servers efficiently, making it suitable for small to enterprise-level environments.
Ansible is a Linux management software best used for:
- Configuration Management: Automating the setup and maintenance of systems, ensuring consistency across your infrastructure.
- Application Deployment: Simplifying the deployment of applications by automating the entire process, from installing dependencies to configuring services.
- Continuous Delivery and Continuous Integration (CI/CD): Integrating with CI/CD pipelines to automate the deployment of code changes and updates.
- Task Automation: Automating repetitive tasks, such as system updates, backups, and user management, freeing up time for more critical activities.
Ansible Cons
- Performance Overhead: Since Ansible is agentless, it can introduce performance overhead on the control node when managing a large number of hosts.
- Complex Error Handling: Error handling in Ansible can be complex and sometimes non-intuitive, requiring careful scripting to manage failures and retries effectively.
Note: To learn how to use Ansible to manage your Linux servers, check out our full Ansible tutorial for beginners.
5) Zabbix
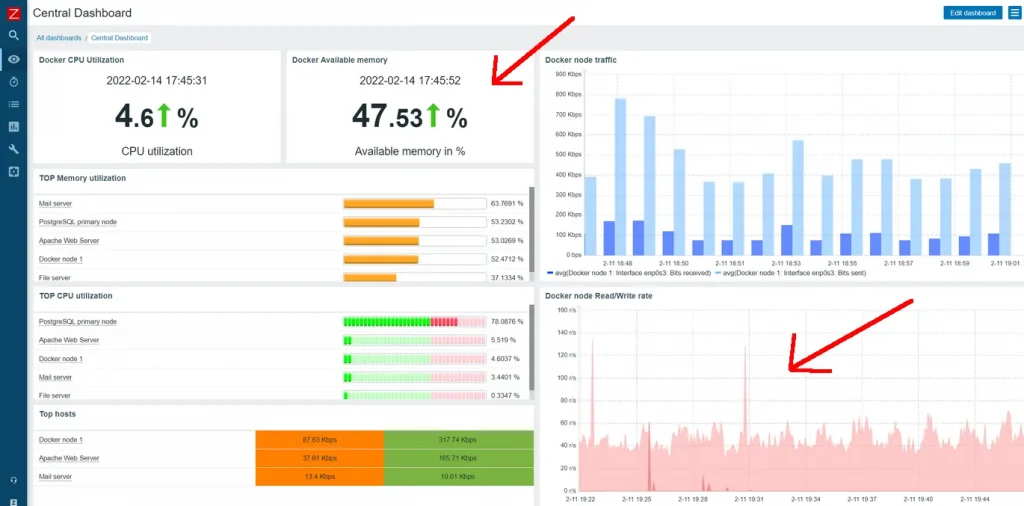
Zabbix is a robust monitoring tool that provides real-time monitoring of servers, networks, and applications. It supports both agent-based and agentless monitoring, offering flexibility depending on your environment. Zabbix’s alerting system and reporting capabilities make it a valuable tool for proactive server management.
Zabbix is a Linux management software best used for:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Track servers, networks, and applications.
- Alerting and Notifications: Receive alerts for issues via email, SMS, or other methods.
- Data Visualization: Create detailed graphs and dashboards.
- Scalable Deployments: Manage large and complex environments efficiently.
- Customizable Checks: Implement custom monitoring scripts and checks.
Zabbix Cons
- Complex Setup: Initial configuration can be time-consuming.
- Steep Learning Curve: Requires significant time to learn and master.
- Resource Intensive: Can be demanding on system resources, especially with large data sets.
- Interface Can Be Overwhelming: The UI has a lot of options, which can be confusing for beginners.
Note: Zabbix has a complex setup, that's why we offer a ready to use Zabbix One-Click Application for our customers. Just visit our website, choose the server’s specifications that fit your needs, then select Zabbix from the Choose OS dropdown menu. Zabbix will then be installed in no time!
6) Puppet
Puppet is a configuration management tool that helps automate the provisioning, configuration, and management of servers. It uses a declarative language to define the desired state of your infrastructure, ensuring consistency and reducing the risk of configuration drift.
Puppet is a Linux management software best used for:
- Configuration Management: Automate the setup and maintenance of systems.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Define infrastructure configurations in code.
- Consistency Enforcement: Ensure system configurations remain consistent over time.
- Scalable Deployments: Manage large-scale environments efficiently.
- Compliance Management: Automate compliance checks and enforcement.
- Change Management: Track and manage changes across your infrastructure.
Puppet Cons
- Complex Setup: Initial setup and configuration can be intricate.
- Frequent Updates Needed: Regular updates and maintenance are necessary.
- Error Debugging Can Be Challenging: Troubleshooting and debugging issues can be complex.
7) Chef
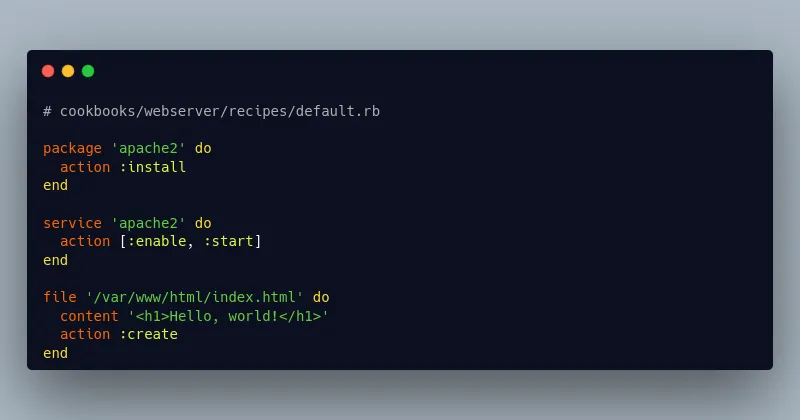
Chef is another powerful configuration management tool that automates the deployment and management of your infrastructure. Using Ruby-based DSL, Chef allows you to write scripts, known as cookbooks, to define how your systems should be configured and maintained.
Chef is a Linux management software best used for:
- Configuration Management: Automate system setup and maintenance.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Define and manage infrastructure through code.
- Automated Deployments: Streamline application deployment processes.
- Scalable Management: Handle large and complex environments efficiently.
Chef Cons
- Steep Learning Curve: Requires time to learn Ruby and the Chef DSL.
- Complex Setup: Initial configuration can be time-consuming and intricate.
- Resource Intensive: Can be demanding on system resources, especially in large environments.
8) SaltStack
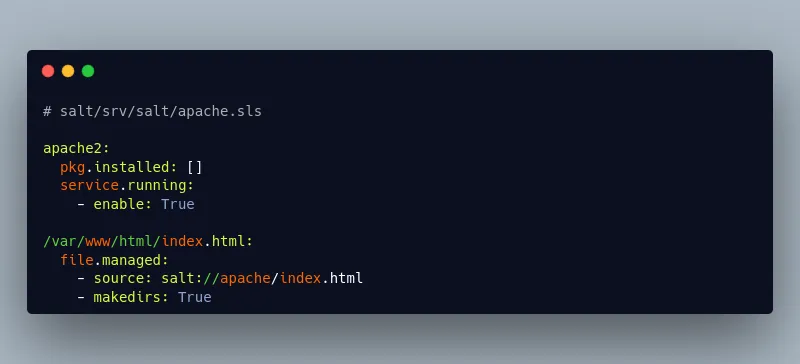
SaltStack is a flexible and scalable tool for configuration management and orchestration. It uses a high-speed, secure communication bus to manage and control servers, allowing for real-time monitoring and execution of commands across your infrastructure.
SaltStack is a Linux management software best used for:
- Configuration Management: Automate system configuration and maintenance.
- Remote Execution: Execute commands and tasks on remote systems.
- Event-Driven Automation: Trigger actions based on system events.
- Scalable Orchestration: Manage large-scale environments efficiently.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Define infrastructure configurations in code.
- Security Automation: Implement security policies and enforce compliance.
SaltStack Cons
- Complex Learning Curve: Mastery of SaltStack's concepts and terminology takes time.
- Documentation Gaps: Some areas of the documentation may lack clarity or completeness.
9) Kubernetes

Kubernetes, while primarily known for container orchestration, also offers powerful tools for managing your Linux servers. It automates the deployment, scaling, and operations of application containers across clusters of hosts, ensuring high availability and efficient resource utilization.
Kubernetes is a Linux management software best used for:
- Container Orchestration: Automate deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
- Service Discovery and Load Balancing: Dynamically manage network traffic to containerized services.
- Resource Utilization Optimization: Efficiently allocate computing resources across containers.
- Self-Healing Capabilities: Automatically recover from container failures and ensure high availability.
- Rolling Updates and Rollbacks: Facilitate seamless updates and downgrades of applications.
- Declarative Configuration: Define application and infrastructure configurations declaratively.
Kubernetes Cons
- Complex Learning Curve: Requires significant time and effort to understand its concepts and components.
- Cluster Setup Complexity: Initial cluster setup and configuration can be challenging.
- High Operational Overhead: Managing and operating Kubernetes clusters may require dedicated personnel.
10) Grafana
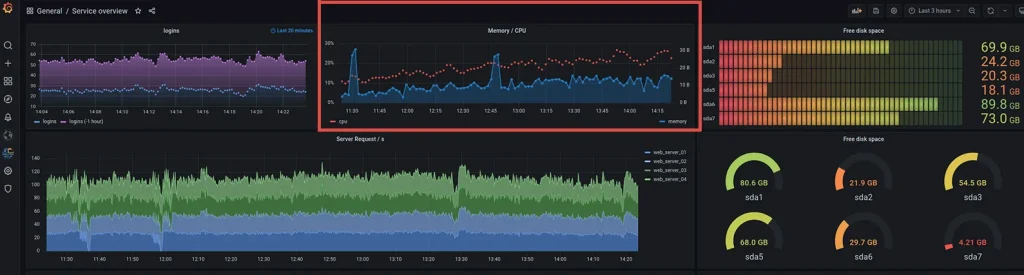
Grafana is an open-source analytics and monitoring platform that integrates with a variety of data sources, including Prometheus. It provides beautiful and customizable dashboards that help you visualize metrics and gain insights into your server performance.
Grafana is a Linux management software best used for:
- Data Visualization: Create customizable and interactive dashboards to visualize data.
- Metrics Monitoring: Collect and display metrics from various sources in real-time.
- Alerting and Notification: Set up alerts based on metric thresholds and receive notifications.
- Data Analysis: Analyze and explore data through ad-hoc queries and visualizations.
- Cross-Platform Support: Compatible with a wide range of data sources and databases.
- Customization and Extensibility: Customize dashboards and extend functionality through plugins.
Grafana Cons
- Configuration Complexity: Setting up Grafana and configuring data sources may require technical expertise.
- Resource Consumption: Can consume significant system resources, especially with large datasets or complex dashboards.
- Alerting Limitations: Alerting features may be limited compared to dedicated monitoring solutions.
Note: To make setting up Grafana as easy as possible, we offer a ready to use Grafana One-Click Application for our customers. Just visit our website, choose the server’s specifications that fit your needs, then select Grafana from the Choose OS dropdown menu. Grafana will be installed in no time!
11) Prometheus
Prometheus is an open-source monitoring and alerting toolkit designed for reliability and scalability. It collects metrics from configured targets at given intervals, evaluates rule expressions, displays results, and triggers alerts when specified conditions are observed.
Prometheus is a Linux management software best used for:
- Monitoring and Alerting: Collect metrics from various sources and set up alerts based on defined thresholds.
- Time-Series Database: Store and query time-series data efficiently for monitoring purposes.
- Scalability: Scale horizontally to handle large volumes of metrics from diverse sources.
- Service Discovery: Automatically discover and monitor new services as they are deployed.
- Robust Query Language: Use Prometheus Query Language (PromQL) to perform complex queries and aggregations.
- Integration with Grafana: Seamlessly integrate with Grafana for data visualization and dashboarding.
Prometheus Cons
- Complex Setup: Initial setup and configuration can be challenging, especially for complex environments.
- Lack of Long-Term Storage: Designed primarily for short-term metric storage. Prometheus's storage is optimized for performance and efficiency, not long-term durability.
- Limited High Availability: High availability configurations can be complex to set up and maintain.
12) phpMyAdmin
phpMyAdmin is a free software tool written in PHP, designed to handle the administration of MySQL and MariaDB over the web. It provides an intuitive interface for database management, allowing users to perform a variety of tasks such as creating databases, running SQL queries, and managing users and permissions. phpMyAdmin simplifies the process of managing MySQL databases directly from your browser.
phpMyAdmin is a Linux management software best used for:
- Web-Based Interface: Manage MySQL databases through an intuitive web interface.
- SQL Execution: Write, execute, and debug SQL queries directly in the browser.
- Database Administration: Perform administrative tasks such as creating and deleting databases, tables, and indexes.
- User Management: Add and manage database users and their permissions.
- Backup and Import: Export and import database structures and data for backup and migration.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Accessible from any device with a web browser, making it platform-independent.
phpMyAdmin Cons
- Security Risks: Being web-based, it can be a target for attacks if not properly secured.
- Performance Limitations: May struggle with performance issues when handling very large databases.
- Limited Advanced Features: Some advanced database management features are less comprehensive than those in dedicated desktop applications.
- Dependency on Web Server: Requires a web server (like Apache or Nginx) to run, adding complexity to the setup.
Note: To make installing phpMyAdmin as easy as possible, we offer a ready to use phpMyAdmin One-Click Application for our customers. Just visit our website, choose the server’s specifications that fit your needs, then select phpMyAdmin from the Choose OS dropdown menu. phpMyAdmin will be installed on your server in minutes!
Tips for Linux Management
Managing Linux servers effectively requires a combination of good practices, tools, and a proactive approach to system administration. Here are some essential tips to help you manage your Linux environment efficiently:
- Regular Updates and Patching:
- Keep your system and applications up to date with the latest security patches and updates.
- Use package management tools like
apt,yum, ordnfto automate updates.
- Automated Backups:
- Implement regular automated backups of critical data and configurations.
- Use tools like
rsync,tar, or dedicated backup software to ensure data integrity.
- Monitoring and Alerting:
- Deploy monitoring tools like Nagios, Zabbix, or Prometheus to keep track of system performance and health.
- Set up alerts for critical events to proactively address potential issues.
- Configuration Management:
- Use configuration management tools such as Ansible, Puppet, or Chef to automate system configuration and deployment.
- Maintain consistency across your servers and reduce configuration drift.
- Security Best Practices:
- Implement strong password policies and use SSH keys for authentication.
- Regularly audit system logs and user activities to detect and respond to security incidents.
- Use firewalls (e.g.,
iptables,firewalld) to restrict unnecessary network access.
- Resource Optimization:
- Monitor and optimize resource usage (CPU, memory, disk) to ensure optimal performance.
- Use tools like
top,htop, andvmstatto identify and troubleshoot resource bottlenecks.
- Documentation and Version Control:
- Document system configurations, procedures, and troubleshooting steps.
- Use version control systems like Git to track changes to configuration files and scripts.



